Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD)
 The Basics
The Basics
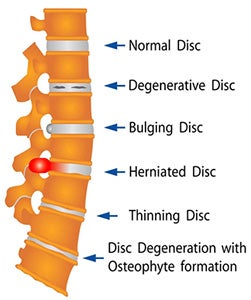
Degenerative Disc Disease is a progressive deterioration of the cushion-like discs between our vertebrae and is considered part of the normal aging process.
The disc’s function is to act as a shock absorber between vertebrae, keeping the spine stable and erect. With repetitive motion and force, the disc can become compressed, putting pressure on surrounding nerves and tissues. This narrowing of space is what can cause pain.
By age 35, approximately 30% of people will show evidence of disc degeneration; by age 60, more than 90% of people will have some form of deterioration within the spine.
Location
The cervical (neck) and lumbar (low back) regions are the most common sites for disc degeneration but deterioration can occur anywhere within the spine.
Symptoms
 Degeneration itself is normal, and does not necessarily cause pain. However, the term ‘Degenerative Disc Disease’ is used to describe disc degeneration that causes pain and other symptoms. Some of the more common are:
Degeneration itself is normal, and does not necessarily cause pain. However, the term ‘Degenerative Disc Disease’ is used to describe disc degeneration that causes pain and other symptoms. Some of the more common are:
- Dull, Continuous, Achy Pain
- Increased Pain with Bending/Twisting/Standing
- Muscle Tension or Spasms
Causes
Degenerative Disc Disease is a progressive deterioration of the cushion-like discs between our vertebrae and is considered part of the normal aging process.
The disc’s function is to act as a shock absorber between vertebrae, keeping the spine stable and erect. With repetitive motion and force, the disc can become compressed, putting pressure on surrounding nerves and tissues. This narrowing of space is what can cause pain.
By age 35, approximately 30% of people will show evidence of disc degeneration; by age 60, more than 90% of people will have some form of deterioration within the spine.
Treatments
Degenerative Disc Disease is typically managed conservatively and often includes one or more of the following treatments:
- physical therapy and activity modification
- heat and/or ice packs
- anti-inflammatory medications including NSAIDs (Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs)
- Steroid medications
- Epidural or other types of injections
Alternative treatments may include massage, acupuncture, acupressure or chiropractic manipulation.
Rarely is surgery performed for degeneration alone, however, there are several conditions of the disc that may require more aggressive care.
